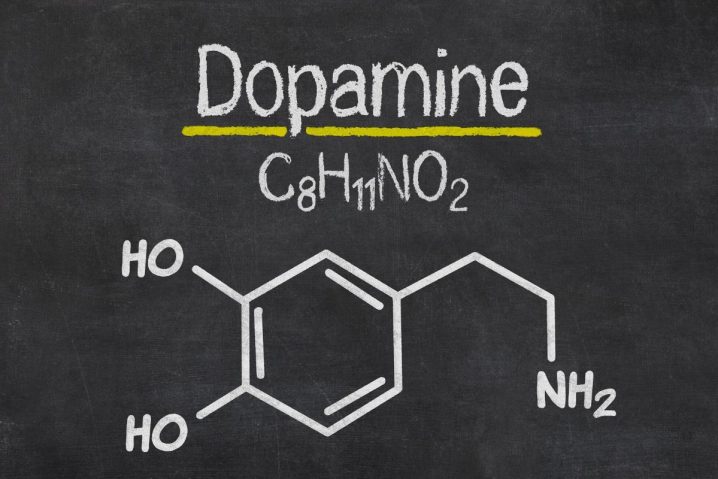
Dopamine is a naturally occurring neurotransmitter that sends signals to and from the parts of the brain that control our focus and mood and several other factors. There are prescription medications such as Adderall and Ritalin and many illicit chemicals that affect the brain’s production of dopamine.
What is Dopamine High?
When any of these chemical substances are taken in large enough doses, it dramatically increases the release of this neurotramsmitter within a short time. In as little as a few seconds, certain drugs’ consumption can produce a euphoric, pleasurable sensation. This sensation is known as a dopamine high.
A dopamine high is a highly addictive experience. It also has the potential to cause numerous other harmful effects. Those who experience a euphoric high may find themselves trying to “chase” the high. As tolerance develops, they may search for more potent stimulants or use more significant amounts to achieve the same effects.
Drugs That Increase Dopamine
There is a wide array of drugs that increase the release of dopamine. As mentioned above, some of them are pharmaceutical drugs, whereas others are illicitly made. Illicit drugs are always dangerous as there is no way to know their exact composition, but even prescription medications should not be taken in doses greater than prescribed.
Prescription Drugs
- Marijuana
- Opioids (OxyContin, Percodan, Percocet, Vicodin, Dilaudid, & methadone)
- Stimulants (i.e., Dexedrine, Adderall, Ritalin®, Concerta®)
Illicit Drugs
- Cocaine
- Marijuana
- MDMA
- Methamphetamine
- Opioids (ie: Heroin & Fentanyl)
Another substance that affects dopamine production and is legal, but is not prescription, is alcohol. An easily accessible and legal substance, alcohol is arguably one of America’s most dangerous mind-altering drugs.
Side Effects
When naturally occurring, dopamine can help increase focus, motivation, mood and regulate sleep. It can also affect heart rate, blood vessel function, kidney function, and lactation. Although pharmaceutical drugs that affect brain chemistry can help control these same functions when an imbalance is present, abuse can create an imbalance and cause severe side effects. When large doses are consumed and a dopamine high occurs, it can lead to dangerously high body temperature, heart failure, seizures, and death.
Resetting Dopamine Receptors
When dependence is developed from long-term substance use that artificially increases dopamine production in the brain, the number of dopamine receptors decreases overtime to compensate for the increase in dopamine available to bind to them.
When substance use is discontinued, it can take some time for the number of these receptors to regrow. As there are initially fewer neurotransmitters and fewer receptors, it is less likely the two will find each other and bind. This leads to depression, a lack of motivation, an increase in cravings, and potentially a substance-induced anxiety disorder. The first few days are the hardest and are why medical detox facilities are ideal for those addicted to drugs affecting brain chemicals.