The effects of alcohol on your body are short and long-lived. However, when you stop drinking alcohol, there are many beneficial impacts on your body and overall well-being. Prevalent society challenges like “Dry January” often ask people to stop drinking for 30 days to start the new year alcohol-free. But what happens when you stop drinking alcohol?
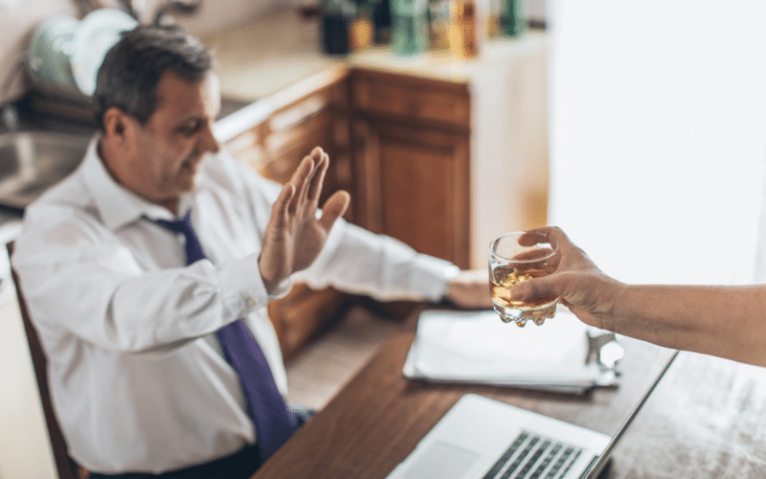
For most people, the idea of cutting out alcohol seems achievable. Saying no to a glass of wine over dinner might seem like a way to avoid empty calories and start living healthier. However, for those with an alcohol use disorder or people engaging in short-term heavy drinking, quitting alcohol is a different challenge.
Still, for recovering alcoholics, avoiding alcohol altogether can have a myriad of health benefits. Although these health benefits vary from person to person, everyone can easily experience them.
What Happens to Your Body When You Stop Drinking?
Whether you frequently drink, engage in binge drinkers, consider yourself a heavy drinker, or are, in reality, an alcoholic, you’ll experience some benefits. As you might know, alcohol abuse increases the risk of liver disease and triggers mental health disorders.
Of course, the differences in symptoms vary tremendously. The health benefits someone experiences will be determined by the amount of alcohol consumed. Someone who has a few wine glasses a month won’t have the same struggles as someone who has more than ten drinks a day.
Quitting drinking can help your body in many incredible ways, including:
- Providing liver relief
- Decreasing your risk of cardiovascular disease
- Reduce your risk of developing cancer, particularly breast cancer
- Promote weight loss
- Boost your brainpower
The First 72 Hours
Day 1 of sobriety, the start of the alcohol detox process, can be very unpleasant for someone who has been drinking heavily for an extended period. As soon as 6 hours after your last drink, alcohol withdrawal symptoms can start to set in.
During this time, the mechanisms in place to manage the body’s alcohol typically receive are still functioning even though there is no alcohol entering the body. When the body has come almost to expect alcohol but doesn’t receive it, it ends with a severe chemical imbalance. It can take a week or more for the human body to re-adjust to an alcohol-free state.
What Happens to Your Body 1 Week After Quitting Alcohol
After about a week of sobriety, the brain and body begin to resume “normal.” The most severe and unpleasant withdrawal symptoms should have subsided. At this time, hormone levels are much more balanced. Additionally, you will find that the midnight thirsts often caused by alcohol-induced dehydration dissipate.
Sleep patterns and sleep quality are significantly improved. No alcohol for one week should mean that the healing is well in its way, and there is much progress occurring in the human body.
After 1 Month of Sobriety
During the first month without drinking, changes occur related to digestive health. Alcohol causes bouts of acid reflux and bloating that are no longer regular occurrences. Additionally, alcohol is rarely a low-calorie substance. The decrease in caloric intake results in significant weight loss over the first month of sobriety.
Blood pressure also rises from alcohol consumption. As a result, noticeable declines in blood pressure happen about 3-4 weeks into sobriety. Lastly, the elasticity of the body’s largest organ, the skin, improves. Someone who stays alcohol-free for a month following heavy alcohol use will begin to look more fresh and healthy simply because of the renewed glow in their skin.
Benefits After Quitting Drinking for 3 Months
Between 1 and 3 months of sobriety is when changes happening at the cellular level are noticeable at the individual level. The liver sustains significant damage from long-term alcohol use. When given the opportunity, this organ is also magnificent at regeneration.
About three months is when one usually needs their liver and cells throughout the body to heal and experience significant change. During this time, energy levels rise, and overall better health begins.
What happens when you stop drinking alcohol for three months is more than physical. For three months, alcoholics in recovery often report positive changes in their emotional state, career, finances, and personal relationships. These reports may include but are not limited to:
- Feelings of depression and anxiety may subside
- Critical thinking skills improve
- Better performance and productivity at work or school
- Increased savings due to a decrease in alcohol purchases
- Improved relationships with family and close friends
Can the Health Impacts of Heavy Drinking Be Reversed?
Some people think that after years of heavy drinking, there’s no point in stopping. In reality, stopping alcohol consumption can significantly reduce the risk of many diseases, including cancer.
Brain Damage
The National Institutes of Health (NIH) reports that former abusers who abstain from alcohol for several months to a year may experience partial correction of some structural changes to the brain. One condition that’s related to long-term alcohol abuse is Wernicke-Korsakoff syndrome or wet brain. This is a condition that could get better when you stop drinking.
Unfortunately, in some cases, damage to your system cannot be reversed. For example, the full extent of the damage produced by chronic and heavy alcohol use on the cardiovascular system is not fully resolved. Most reversed impacts will occur within the first months to the first year of abstinence. Changes in lifestyle factors like diet, exercise, and stress management are key to sustained recovery.
Liver Damage & Ulcers
Another common damage that’s caused by alcohol consumption is liver damage. Research suggests that if individuals begin an abstinence program early enough, mild liver damage may not be serious enough to cause issues. However, when someone develops cirrhosis of the liver, this cannot be rectified by abstinence or lifestyle changes. At this stage, only a liver transplant is possible.
On the same line of liver damage, people who struggle with alcohol consumption also experience ulcers. Unless they are severe, gastritis and ulcers can be reversed through treatment and abstinence from alcohol. However, there will most likely be some scar tissue remaining in the individual’s gastrointestinal tract.
Bone Damage
At last, there’s another condition that alcohol addiction often triggers: osteoporosis. While there’s no cure for osteoporosis, treatment can help stop further damage and reverse some of the effects. Still, refraining from drinking alcohol can help prevent more damage and the onset of other health conditions.
Start Your Recovery Journey Today
If you or someone you know is ready to stop drinking and controlling their substance abuse disorder, contact us today. Remember, alcoholism is a life-threatening condition. Through our comprehensive alcohol abuse treatment programs, we can help you start your journey toward recovery and leave alcohol dependence behind you. Call 866-308-2090 today to start.